Watch the video below to learn more about locking SafeSearch.
You can tell at a glance if the lock is engaged
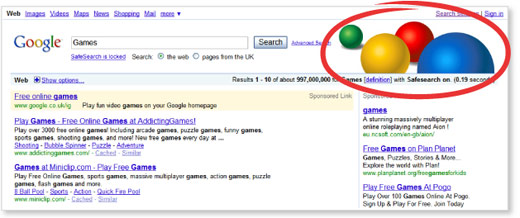
When the SafeSearch lock is on, the top of the search results page looks different in two ways: 'SafeSearch is locked' is displayed below the search box, and the colored balls appear on the right. The results page is designed to look different enough that you can immediately tell whether the lock is on or off -- even from across the room.
Results page when locked
Follow these steps to lock SafeSearch:
1. Visit the Search settings page.
2. Click Lock SafeSearch below the filter levels.
3. If you're not signed in to your Google Account, you'll be prompted to sign in.
(Don't have a Google Account? You can create one.)
4. Once you're signed in, click Lock SafeSearch. This step takes a moment,
because strict filtering is being applied to all Google domains.
5. You'll see a confirmation page once the lock is engaged.
Tips about browsers and settings
* If you have more than one browser on your computer,
you need to set the lock on each one individually.
* If your computer has more than one user profile (for example, a family
computer), you need to set the lock on each appropriate profile.
* Make sure your browser is set to allow cookies.
Using Safari? You may need to change the default setting and enable third-party cookies for the lock to work.
